SELFIEforTEACHERS case studies (JRC/SVQ/2022/MVP/1278 – SELFIEforTEACHERS case studies) is an EU-funded project which was coordinated by the Department of Communication and Internet Studies of the Cyprus University of Technology (CUT). The project was funded by the Joint Research Center (JRC-Seville) of the European Commission and involved the following partners: Cyprus University of Technology, Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, Greece, University of Twente, The Netherlands, University College Dublin, Ireland, Universitat Pompeu Fabra, Spain, and University of Helsinki.
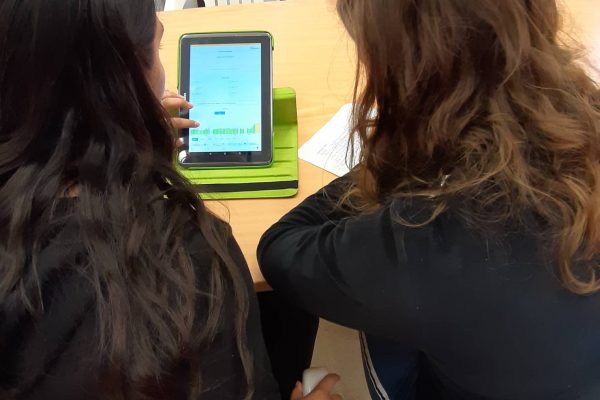
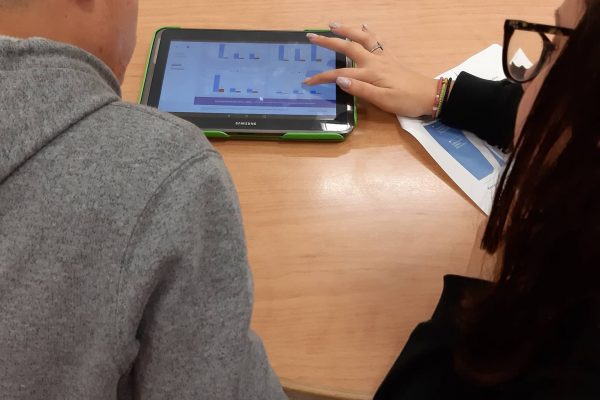
SELFIEforTEACHERS (SfT) is an innovative online tool designed by the European Commission’s Joint Research Center (JRC) to support teachers’ reflection on the use of digital technologies, contributing to the advancement of teachers’ digital competence.
The SELFIEforTEACHERS case studies project focused on the use and empirical exploration of the SfT, aiming at highlighting and empirically documenting the design principles that can contribute to the optimal use of the online tool, in various educational settings. Toward this end, 13 uses cases were designed and empirically validated in the context of 13 qualitative case studies by the project partners.
The project was completed with the preparation and publication of a technical report which provided an overview of the main findings emerged from the cases studies. The project outcomes were also disseminated at various international conferences.
Focus: Investigation of the optimal use of the SELFIEforTEACHERS (SfT) online tool in various educational conexts for the advancement of teachers’ digital competence.
Funding: European-funded project
Status: Completed
Publications
Economou, A., Kyza, E. A., Georgiou, Y., Kapsalis, G., Gallagher, S., Galvin, C., … & Garcia, A. R. (2024). Using self-reflection to support teacher professional learning and development of their digital competence: A multi-case study using SELFIEforTEACHERS. No. JRC138661. Joint Research Centre, 2024.
Economou, A., Kapsalis, G., Kyza, E. A., Georgiou, Y., Gallagher, S., Galvin, C., … & Garcia, A. R. (2024). Building Digital Competence: Personal and Contextual Factors in Teachers’ Professional Learning. In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference of the Learning Sciences-ICLS 2024, pp. 298-305. International Society of the Learning Sciences.
Kyza, E. A, Georgiou, Y., Gallagher, S., Galvin, C., Gonida, S. E., Hernandez-Leo, D, … Kapsalis, G. (2024). From self-reflection to professional agency: personal, contextual, and relational aspects in developing teachers’ digital competence. Paper presented at the Annual Meeting of the American Educational Research Association.